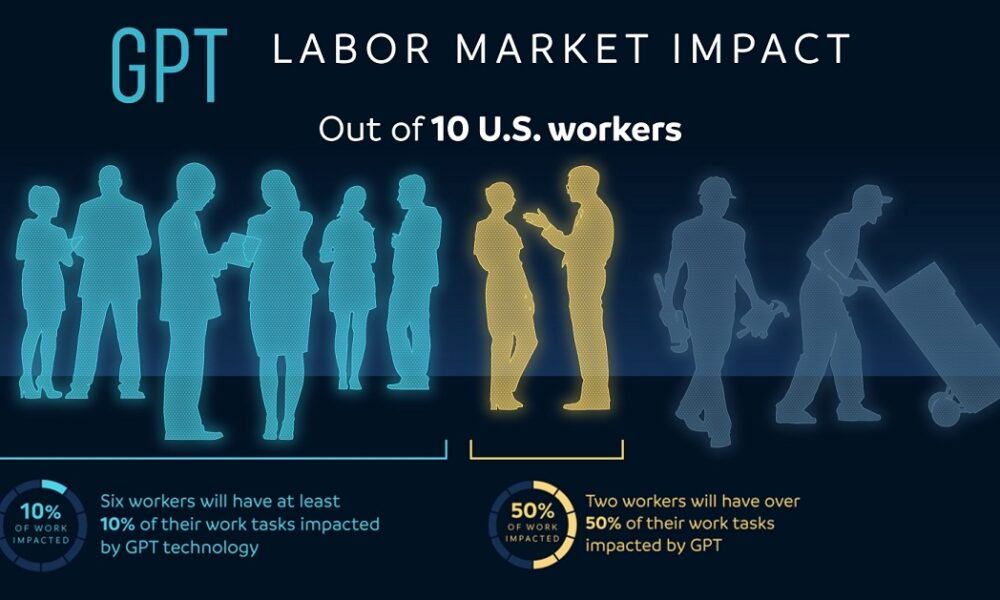
The impact of AI on the labor market is becoming increasingly evident, as recent studies highlight the profound changes that artificial intelligence is ushering into the workforce. Economists David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers have uncovered trends that signal substantial labor market disruptions caused by AI, challenging previous beliefs about job security and stability. Their research demonstrates that while there was a relatively calm period from 1990 to 2017, the shift since 2019 hints at a significant wave of occupational churn driven by advancements in technology. This evolution paints a vivid picture of the future of jobs as AI continues to redefine roles and skill requirements, making it essential for all sectors to adapt. With a focus on technology’s influence in the U.S. labor market, understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating tomorrow’s employment landscape.
Exploring the intersection of artificial intelligence and employment dynamics unveils a new narrative surrounding workforce evolution and job creation. Recent examinations of technological advancements reveal that changes in the labor landscape are inevitable, highlighting the necessity for adaptation among workers. As we analyze the ongoing transformation prompted by emerging technologies, it becomes apparent that the traditional understanding of job roles is being reshaped significantly. The rise of machine learning and automation not only fuels conversations about job displacement but also points towards new opportunities within various fields. Recognizing these shifts is critical for leveraging the benefits of these innovations while minimizing the disruptions they may bring.
The Role of AI in Labor Market Disruptions
Artificial Intelligence is increasingly becoming a significant player in labor market disruptions, influencing job roles across various industries. As outlined in a study by Harvard economists, the advent of AI technologies is not just an incremental change; it represents a seismic shift akin to the introduction of electricity or the keyboard. These innovations have a profound effect, as they reshape job functions and alter the demand for skills. Many workers must now adapt to a faster-paced environment where proficiency with AI tools is no longer optional but necessary for survival in the workforce.
The research indicates that from 2019 onward, the labor market has undergone major shifts spurred by advancements in AI. The study demonstrates a decline in low-paid service jobs while concurrently highlighting a rise in high-skill professions, particularly those in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). Job polarization, where employment opportunities become skewed towards highly-paid and low-paid jobs, is further complicated by AI integration, driving the necessity for reskilling initiatives and educational reforms to prepare the future workforce.
Understanding Occupational Churn in Today’s Economy
Occupational churn, defined as the evolution of job roles through technological advancements, is a crucial aspect of the current economic landscape. Analyzing historical data spanning over a century, researchers discovered a low-churn period from 1990 to 2017, during which employment in various sectors remained relatively stable. However, this stability is now giving way to significant changes brought on by innovations in AI. The study notes that the rate of churn has significantly increased since 2019, revealing a paradox where fears of job loss from automation are being met with an expanding market for highly-skilled jobs.
As the labor market adapts to new technological realities, it becomes clear that the sectors experiencing growth are not merely retraining old roles but are instead focusing on the creation of new occupations that reflect the demands of an AI-driven economy. This necessitates a greater emphasis on STEM education and vocational training tailored to emerging industry needs, emphasizing the importance of adaptability and lifelong learning. By understanding occupational churn, policymakers and educators can better design programs that prepare workers for the jobs of tomorrow.
Emerging Trends Following AI Integration in Jobs
The integration of AI into various sectors is catalyzing notable trends that redefine traditional job markets. According to the findings of the Harvard economists, one significant trend is the shrinking of opportunities in low-wage, low-skill jobs that have historically formed the backbone of service industries. As companies increasingly lean on technology to streamline operations, the demand for manual labor declines. This shift not only impacts employment rates but also drives an increasing wage disparity between low-skilled positions and high-skilled jobs, highlighting the need for strategic workforce planning.
Moreover, the rise in STEM job opportunities post-2019 signifies a pivotal shift in the types of skills that will be essential in the future job market. With a 50 percent increase in jobs related to technology and analytics, industries are pushing toward a model that favors highly-educated and trained individuals who can leverage AI technologies efficiently. This growing emphasis on high-tech skills presents a clear challenge for displaced workers, underscoring the need for targeted educational initiatives to bridge the skills gap and ensure that workers are prepared to compete in an evolving economy.
The Future of Jobs in an AI-Driven World
As artificial intelligence continues to permeate different facets of work, the future of jobs presents both challenges and opportunities. The Harvard study reveals that the landscape of employment is not only changing but evolving to create new job categories that do not yet exist. This change is fueled by the recent trends in job creation across high-wage skilled sectors while simultaneously phasing out traditional roles that are becoming irrelevant due to automation and AI capabilities. Workers will need to embrace a mindset of flexibility to navigate an increasingly uncertain employment landscape.
Anticipating the future job market demands new strategies for both individuals and companies. Workers in various sectors must strive to enhance their technical proficiency and soft skills to stay relevant. Simultaneously, companies need to reassess their hiring practices and invest in employee training to adapt to the rapid technological advancements influencing commerce today. In essence, the successful navigation of the AI-driven job market relies on a proactive approach to learning that aligns with emerging industry needs.
Investment in AI and its Market Effects
The substantial investment in artificial intelligence technology is significantly influencing market dynamics and employment structures. Companies are increasingly allocating resources toward AI initiatives that automate processes, optimize efficiencies, and enhance productivity. These investments not only alter the types of goods and services offered but also redefine the roles and skills deemed valuable in the workforce. According to the findings, firms are not merely adapting to change—they are leading it through strategic innovations that reshape the labor landscape.
As AI technology becomes ingrained in operations, the labor market is experiencing a redistribution of roles, with a declining share of low-paid service jobs simultaneously coinciding with the rise of tech-centric positions. Organizations that invest in AI are also enforcing new skill requirements, pushing employees to evolve and adapt. As highlighted by the study, firms treating AI as a functional tool for growth indicate a broader trend towards embracing technology as not just a means to an end, but as an integral component of corporate strategy and workforce development.
AI’s Impact on Knowledge Workers
The advent of AI technologies presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities for knowledge workers in various industries. Professionals in fields such as finance, journalism, and management are beginning to reassess their roles and productivity expectations in an AI-enhanced environment. The expectation is shifting towards a greater reliance on efficiency and speed, with organizations increasingly demanding quicker outputs due to AI’s availability. As such, knowledge workers must adapt to these heightened expectations while simultaneously leveraging AI as a tool that can augment their capabilities.
The integration of AI not only enhances productivity but also introduces competitive pressure among knowledge workers, emphasizing the need for continuous learning and adaptation. As indicated by Harvard’s research, organizations will likely prioritize hiring those who are adept at utilizing AI technologies, placing additional importance on upskilling initiatives. Moving forward, knowledge workers will need to cultivate a balance between human creativity and AI-enhanced efficiency to thrive in an environment that increasingly seeks productivity gains through technological advancements.
Addressing Automation Anxiety in the Workforce
Automation anxiety has been a prevailing concern among workers in the wake of increasing artificial intelligence capabilities. The fear that AI will lead to significant job loss and market instability has been a critical point of discussion in labor studies. However, the Harvard economists’ findings challenge this narrative, revealing that the pace of job displacement due to automation has seen fluctuations rather than a straightforward decline. This indicates that while some roles are being automated, new positions are emerging, necessitating a constructive conversation about the role of upskilling and job creation.
Organizations and policymakers must work collaboratively to address these anxieties by implementing support systems that encourage training and reskilling as technology advances. In particular, raising awareness about the evolving nature of jobs and emphasizing the opportunities that AI technology can provide might mitigate fears. Both educational institutions and companies should invest in training programs that equip employees with the knowledge needed to navigate the changing landscape, fostering an environment where adaptation and innovation meet emerging technological capabilities.
Strategies for Workforce Reskilling and Adaptation
As the labor market continues to evolve in response to advancements in artificial intelligence, effective strategies for reskilling and adaptation become increasingly crucial. Workers impacted by AI-induced changes need targeted retraining programs to transition into the high-skilled positions that are rising in demand. This requires collaboration between businesses, educational institutions, and government entities to create comprehensive pathways that address the skills gap and prepare workers for future job opportunities in high-tech sectors.
Moreover, a focus on lifelong learning is essential in a rapidly changing labor market. Individuals must embrace continuous training not only to enhance their employability but also to maintain relevance in a technology-driven workplace. Organizations can foster a culture of upskilling by offering internal training programs that emphasize AI literacy, data analytics, and technical skills. By creating environments that support learning and adaptation, both employers and employees can thrive in the face of ongoing technological disruption.
Navigating Economic Inequities in an AI-Driven Labor Market
The integration of artificial intelligence into the labor market highlights existing economic inequities and presents challenges that need to be addressed proactively. As AI adoption accelerates, the divide between high-wage, skilled positions and low-wage, unskilled roles widens, further exacerbating socioeconomic disparities. It is critical for policymakers to develop inclusive strategies that ensure equitable access to training and education for all workers, particularly those from disadvantaged backgrounds, to avoid leaving vulnerable populations behind.
Additionally, addressing these inequities requires a multi-faceted approach, including investments in community-based educational programs that focus on technology and analytics skills. By bridging the skills gap, we can create pathways for underrepresented demographics to gain access to emerging job opportunities. Discussions surrounding AI’s impact must encompass strategies that promote economic inclusivity, ensuring that technological advancements benefit society as a whole rather than creating divides that hinder progress.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is AI impacting the labor market?
AI is significantly altering the labor market by introducing occupational churn, particularly in fields like science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM). Research shows that investment in AI is spurring demand for high-skilled workers while reducing opportunities in lower-paid service jobs, indicating that AI is creating both new roles and eliminating existing ones.
What are the trends in labor market disruptions due to AI?
Recent studies highlight four key trends due to AI’s impact on the labor market: 1) The resurgence of demand for high-skilled jobs, particularly in STEM fields. 2) A decline in low-paid service jobs post-2019. 3) A notable fall in retail sales jobs driven by technological advancements, notably e-commerce. 4) The end of job polarization where low-paid jobs grew without corresponding increases in middle-paid jobs.
Will AI cause significant job displacement in the U.S. labor market?
While AI is expected to displace certain jobs, particularly in low-wage sectors, it is also creating new opportunities for high-skilled positions. The evolving nature of work suggests that AI will disrupt the labor market but will not uniformly eliminate jobs; rather, it will change the types of skills demanded by employers.
What does the future of jobs look like with the rise of AI?
The future of jobs in an AI-influenced labor market is likely to be shaped by higher demand for technical skills, particularly in STEM areas. As AI continues to integrate into workplaces, workers may need to adapt and upskill to remain competitive. AI could lead to increased productivity but also necessitates a shift in how labor is organized and the types of roles available.
What role does technology play in U.S. labor market changes?
Technology, especially AI, has been a catalyst for substantial shifts in the U.S. labor market over the past century. The introduction of AI and automation influences employment patterns, leading to a demand for more skilled labor while simultaneously causing disruptions in traditional low-wage jobs and service sectors.
How has occupational churn changed with advances in AI?
Occupational churn in the U.S. labor market has shown signs of volatility since 2019, attributed partly to AI and other technological advancements. This denotes a faster turnover in job vacancies and a shift towards greater demand for high-skill roles, while low-skill jobs face a decline.
Can AI be considered a ‘breakthrough technology’ in the labor market?
Yes, AI is seen as a breakthrough technology much like the advent of keyboards or electricity, significantly impacting job availability and skill requirements. Its integration into various industries is reshaping the structure of the labor market, necessitating new skills and altering employment landscapes.
What can workers do to prepare for the changes brought by AI in the labor market?
To prepare for the changes caused by AI, workers should focus on continuous learning and upskilling in areas like technology and data analysis. Embracing adaptability and agility within their careers will be crucial as AI technologies evolve and reshape various job roles.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Overview | Examines AI’s impact on the U.S. labor market over 100 years, highlighting trends and shifts in occupational churn. |
| Historical Perspective | Stable labor market from 1990 to 2017, challenging the belief that robots are stealing jobs. |
| Recent Trends | Shift toward automation and AI identified post-2019, revealing increasing volatility in job distribution. |
| Job Polarization | Emerging trend favoring high-skilled, well-paid jobs, reversing the job polarization trend of the 2000s. |
| STEM Job Surge | Significant increase in STEM jobs from 2010 to 2024, reflecting a growing demand for technical skills. |
| Decline in Low-Paid Jobs | Stagnation or decline in low-paid service work since 2019, with less demand for retail jobs due to technology. |
| Investment in AI | Companies are investing heavily in AI, impacting job distribution and employment trends. |
| Future Outlook | AI expected to boost productivity but may lead to displacement of less tech-savvy workers. |
Summary
The AI impact on the labor market is profound, as a recent study sheds light on how technology has transformed job roles and employment dynamics over the last century. Researchers have uncovered emerging trends highlighting a shift toward high-skilled positions and an increasing adoption of AI in various sectors. These changes, initiated after 2019, indicate a decline in low-paid jobs, particularly in retail, while STEM-related occupations are on the rise. As companies embrace AI, the labor market may see a further divergence in job distribution, emphasizing the importance for workers to adapt to technological advancements. The findings serve as a crucial reminder that while AI holds the potential for productivity boosts, it also poses a risk of displacing those unprepared for the evolving demands of the job market.